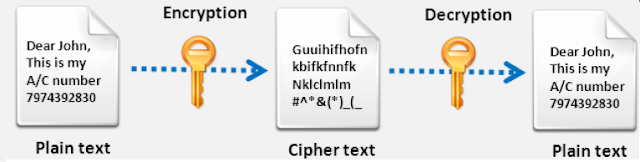
- Data encryption translate data into another form or code so that only people with access to a secret key or password can read it.
- Encrypted data commonly referred to as cipher text while un-encrypted data is called plain-text.
- Currently encryption is one of the most popular and effective data security methods used by organization.
Types:
Symmetric Encryption:
- It is also called private key cryptography.
- Same key used to encrypt and decrypt.
- Faster compare to asymmetric encryption.
- The problem with this method of encryption is order for data to be decrypted, the key must be available.
- This causes two problems 1st problem is the key needs to stored securely.
- If attacker were to gain access to this key they could decrypt any data that key was used to encrypt.
- 2nd problem is secure channel required to transfer the key.
Asymmetric Encryption:
- It is also called as public key cryptography.
- Used both public and private keys.
- Slower compare to symmetric key.
- With this method, a public key is freely available to everyone and is used to encrypt message, and different private key is used by recipient to decrypt message.
How Encryption Work:
- Encryption is an interesting piece of technology that works by scrambling data so it is unreadable by unintended parties.
- Say i want to send you a private message, so i encrypt it using either one of the technologies.
- Once encrypted, the message literally becomes a jumbled mess of random characters. But equipped with the secret passcode.
- You can decrypt it and find the original message.
 |
| Encrypted Data |
 |
| Decrypted Data |
- Triple DES
- RSA
- Blowfish
- PGP
- Twofish
- AES
Advantages:
- Secure the data.
- Identity theft protection.
- Unauthorized Access protection.
Disadvantages: