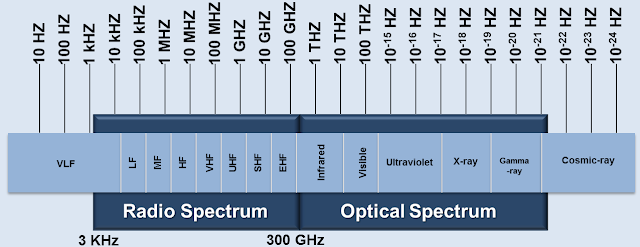
Frequency Spectrum:
- Frequency spectrum is a scientific method of plotting and classifying electromagnetic waves as occur in space and in the every day environment.
Applications:
| FREQUENCY | APPLICATION |
| Hz | Hertz |
| 0 | Earth magnetic field, DC power transmission |
| 16 | Power supply for electric trains in Europe |
| 50 | Power supply system in Europe |
| 60 | Power supply system in the United States |
| 400 | Power supply in airplanes |
| KHz | KiloHertz |
| 10 – 150 | Military, government communication |
| 470 – 700 | TV channels |
| 728 – 798 | New cellular band (2009), previously TV channels |
| 806 – 821 | SMR uplinks |
| 1990 – 2110 | Broadcast studio to transmitter link |
| 2110 – 2170 | New cellular phone band (WCDMA 2100) |
| GHz | GigaHertz |
| 4 – 6 | Future satellite TV |
| 5.14 – 5.70 | WLAN |
| 5.8 | New cordless phones |
| 11.7 – 12.7 | Satellite TV, small dish |
| 28 – 29 | Future wireless TV |
2G technology:
- It is refers to the 2nd generation which is based on GSM.
- Originally designed on 900MHz range, now also available on 800MHz and 1900MHz ranges.
- 2G network use digital signals.
- Its data speed was upto 64Kbps.
- It enables text, picture messages and MMS.
- It provides better quality and capacity.
Drawbacks:
- Unable to handle complex data such as videos.
- data speed is low.
3G technology:
- It is refers to the 3rd generation which is based on UMTS band.
- It range 900MHz, 2100MHz.
- Data transmission speed increased from 144kbps-2Mbps.
Features of 3G:
- High speed web/More security.
- Video conferencing/3D gaming.
- TV streaming.
- high speed download.
Drawbacks:
- Expensive fees for 3G licenses services.
- High band width requirement.
- Large cell phone.
4G technology:
- It is refers to the 4th generation.
- Its range FD-LTE in 1800MHz, and TD-LTE in 2300MHz.
- The data speed is 100Mbps-1Gbps.
Features of 4G
- High speed.
- High capacity.
- More security.